Distinguishing Between Flat Knitting Machines and Circular Knitting Machines
Dec 18, 2023
In the realm of textile manufacturing, knitting machines play a crucial role in the efficient production of various fabrics. Among the various types of knitting machines, flat knitting machines and circular knitting machines stand out as the common choices for manufacturers worldwide. While both variants share the common goal of creating knitted fabrics, they exhibit significant differences in design, functionality, and applications. This article delves into the intricacies of flat knitting machines and circular knitting machines, exploring their fundamental distinctions and emphasizing their respective advantages and limitations.
Circular Knitting Machines:
As the name suggests, circular knitting machines operate in a continuous circular motion. These machines are specifically designed for the production of fabrics like T-shirts, jersey fabric, and sportswear. Unlike flat knitting machines that move needles horizontally and vertically, circular machines use a circular needle bed to transform yarn into a continuous tubular fabric.
Design and Functionality: Circular knitting machines consist of a cylinder, commonly referred to as the knitting head, containing numerous rows of needles arranged in a circular formation. Yarn is fed into the needles through sinkers and guides. As the cylinder rotates during knitting, it continues to form a tubular fabric.
Applications: Circular knitting machines excel in fabric production and are highly sought after for products such as T-shirts, leggings, sportswear, and similar apparel. They are also popular in the production of socks, hosiery, and various elastic fabrics.
Advantages:
- High Production Speed: Circular knitting machines are renowned for their high-speed production capabilities, making them an ideal choice for bulk fabric manufacturing.
- Overall Fabric Design: Due to the circular motion of large circular machines, they can easily produce extensive overall fabric designs.
Limitations:
- Limited Design Patterns: While circular machines excel at creating overall designs, they are less adept at intricate, detailed patterns.
- Yarn Consumption: Circular machines often consume more yarn compared to flat knitting machines, potentially increasing material costs and waste.
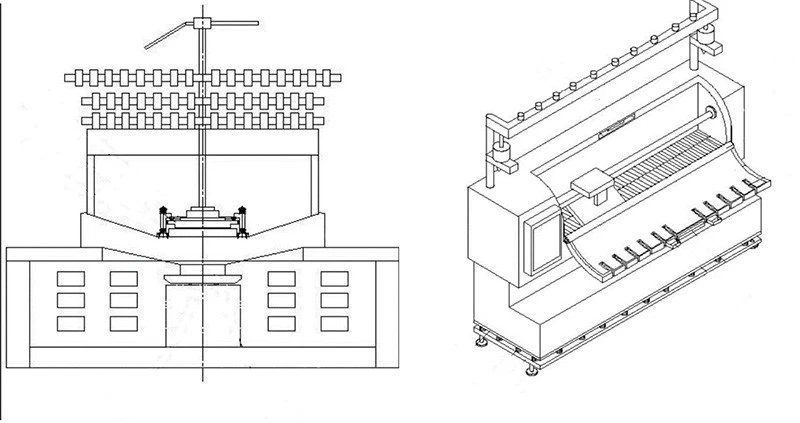
Flat Knitting Machines:
Flat knitting machines are renowned for their versatility and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to effortlessly create complex patterns and designs. These machines operate by fixing yarn onto a flat surface, forming flat knitted fabric panels by horizontally and vertically moving needles.
Design and Functionality: Flat knitting machines typically consist of a needle bed, carriage, and guides. The needle bed features many narrow slots or grooves as the foundation for knitting needles. Each needle is manipulated through a cam system or computer control, allowing precise control over pattern formation. The carriage is responsible for horizontally moving the knitting needles across the bed, while guides accurately feed the yarn into the needles to form the fabric.
Applications: The versatility of flat knitting machines makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. From producing intricate patterns and designs for shawls, sweaters, and dresses to creating seamless garments, flat knitting machines are a popular choice in the fashion industry. Their flexibility also makes them suitable for manufacturing interior decor, automotive interiors, and home textiles.
Advantages:
- Design Flexibility: Flat knitting machines offer precise control over pattern formation, making them ideal for complex designs and patterns.
- User-Friendly: These machines provide a user-friendly operation, making them accessible to both skilled craftsmen and beginners.
- Efficient Yarn Usage: Flat knitting machines maximize yarn utilization, minimizing material waste and potentially reducing production costs.
Limitations:
- Limited Width: The characteristics of flat knitting machines restrict the width of the fabric they produce, making them less suitable for extensive overall designs.
- Time-Consuming: Creating large fabric panels on flat knitting machines can be time-consuming, especially when compared to alternative fabric production methods.
Conclusion: In textile manufacturing, both flat knitting machines and circular knitting machines play crucial roles. The choice between the two largely depends on the desired fabric structure, design complexity, and production scale. Flat knitting machines offer outstanding versatility for intricate designs and patterns, while circular machines master the production of seamless tubular fabrics. By understanding the complexities and differences between these two types of knitting machines, manufacturers can make informed decisions on incorporating the most suitable knitting machine into their manufacturing processes, ultimately delivering high-quality textiles to consumers worldwide.
Prochain: Analyse et solution des défauts courants des tissus tricotés en chaîne
previous: Analysis and Prevention of Horizontal Bars in Knitted Fabrics
